CAPTCHA is a significant web scraping obstacle that lets humans through and keeps bots out. But today, we'll see how Puppeteer helps you overcome that technology and what you can do to make it more effective.
In brief, the methods to bypass CAPTCHA with Puppeteer are:
- Use a paid solver.
- Implement a free solver.
- Mask base Puppeteer.
- Mask your requests.
Let's get started!
Can Puppeteer Solve CAPTCHA?
Short answer: Yes, it can!
The full answer is there are two main approaches: avoiding and solving it.
Since the challenge is prompted mostly based on suspicious activity, and headless browsers help web scrapers mimic human behavior, Puppeteer helps us avoid it. However, we'll need to supercharge base Puppeteer to increase its success rate.
Yet, the most straightforward scenario is when the challenge is prompted, and you just want to solve it. For this, you'll have to use a third-party solver with Puppeteer.
This tutorial will cover both approaches to help you bypass CAPTCHA with Puppeteer.
Method #1: Use a Paid CAPTCHA Solver with Puppeteer
Let's imagine you encounter a CAPTCHA-protected form while scraping and need to solve it. Here, we'll use 2Captcha, an API-based service that employs humans to solve the challenge and returns the answer.
2Captcha's demo page is the sandbox we'll use to illustrate how to integrate the solver with Puppeteer from scratch.
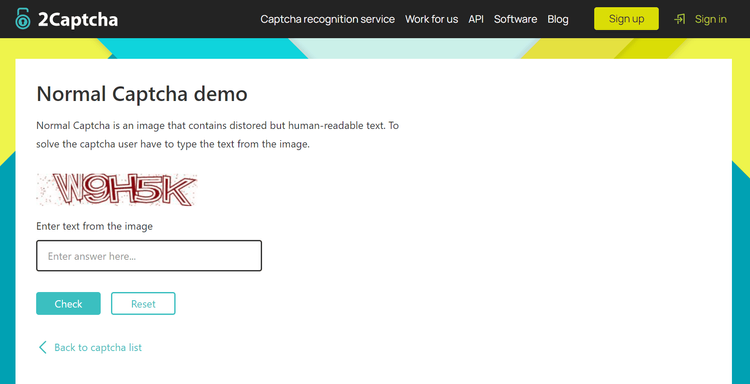
First of all, sign up on 2Captcha to get an API key. Then, install Puppeteer and the requests module.
npm install puppeteer request
Now, let's write a script that opens the website you want to scrape, takes a screenshot of the CAPTCHA and sends it to the service.
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
const request = require('request');
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch();
const page = await browser.newPage();
// navigate to the page with the CAPTCHA
await page.goto('https://2captcha.com/demo/normal');
// take a screenshot of the CAPTCHA
const screenshot = await page.screenshot();
// convert the screenshot to a base64 encoded string
const image = new Buffer(screenshot).toString('base64');
// send the image to the 2Captcha API
request.post({
url: 'http://2captcha.com/in.php',
formData: {
key: 'your_2captcha_api_key',
method: 'base64',
body: image
}
}, async (error, response, body) => {
if (error) {
console.error(error);
}
We'll capture the API response, as shown below, using an ID.
// get the CAPTCHA ID from the 2Captcha API response
const captchaId = body.split('|')[1];
// request the CAPTCHA solution from the 2Captcha API
request.get({
url: `http://2captcha.com/res.php?key=your_2captcha_api_key&action=get&id=${captchaId}`
}, (error, response, body) => {
if (error) {
console.error(error);
}
});
Once we get the solution, we can put it on the page to solve the test.
// get the CAPTCHA solution from the 2Captcha API response
const captchaSolution = body.split('|')[1];
// use the CAPTCHA solution in your Puppeteer script
await page.type('#captcha-input', captchaSolution);
await page.click('#submit-button');
This is what our full script looks like:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
const request = require('request');
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch();
const page = await browser.newPage();
// navigate to the page with the CAPTCHA
await page.goto('https://example.com/captcha');
// take a screenshot of the CAPTCHA
const screenshot = await page.screenshot();
// convert the screenshot to a base64 encoded string
const image = new Buffer(screenshot).toString('base64');
// send the image to the 2Captcha API
request.post({
url: 'http://2captcha.com/in.php',
formData: {
key: 'your_2captcha_api_key',
method: 'base64',
body: image
}
}, async (error, response, body) => {
if (error) {
console.error(error);
} else {
// get the CAPTCHA ID from the 2Captcha API response
const captchaId = body.split('|')[1];
// request the CAPTCHA solution from the 2Captcha API
request.get({
url: `http://2captcha.com/res.php?key=your_2captcha_api_key&action=get&id=${captchaId}`
}, async (error, response, body) => {
if (error) {
console.error(error);
} else {
// get the CAPTCHA solution from the 2Captcha API response
const captchaSolution = body.split('|')[1];
// use the CAPTCHA solution in your Puppeteer script
await page.type('#captcha-input', captchaSolution);
await page.click('#submit-button');
}
await browser.close();
});
}
});
})();
Are you excited about the results? Here they are:
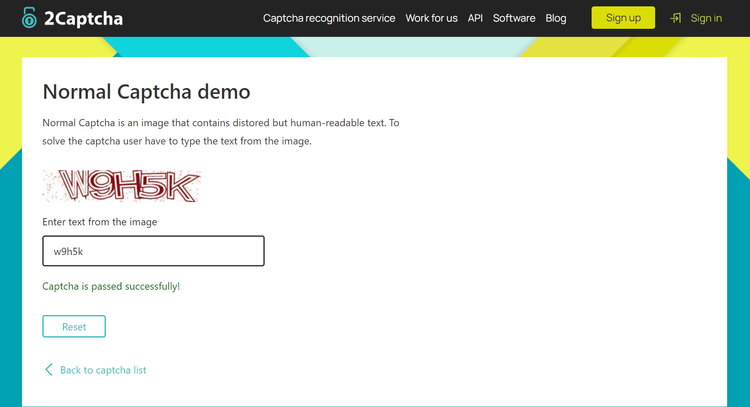
Voilà! 🎉 You solved your first CAPTCHA using Puppeteer and 2Captcha.
The problem is this service gets expensive and slow when scraping at scale. Also, there are some types of CAPTCHAs that can't be solved by API solvers.
Method #2: Implement a Free Solver Plugin
puppeteer-extra-plugin-recaptcha is a free and open-source module that automates the solving of reCAPTCHA and hCAPTCHA, two of the most popular anti-bot technologies on the market. Also, it comes with a 2Captcha integration so that you'll be able to use it in cases when the free module isn't enough.
We'll play with the same demo page as a sample target.
To get started, install puppeteer-extra and recaptcha.
npm install puppeteer puppeteer-extra puppeteer-extra-plugin-recaptcha
Import the libraries and provide your 2Captcha API key as a token.
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer-extra')
const RecaptchaPlugin = require('puppeteer-extra-plugin-recaptcha')
// Use the RecaptchaPlugin with the specified provider (2captcha) and token
puppeteer.use(
RecaptchaPlugin({
provider: {
id: '2captcha',
token: 'XXXXXXX'
},
visualFeedback: true // Enable visual feedback (colorize reCAPTCHAs)
})
)
Next, navigate to your target webpage and initialize the solving with the page.solveRecaptchas() method.
// Launch a headless browser instance
puppeteer.launch({ headless: true }).then(async browser => {
// Create a new page
const page = await browser.newPage()
// Navigate to a page containing a reCAPTCHA challenge
await page.goto('https://2captcha.com/demo/recaptcha-v2')
// Automatically solve the reCAPTCHA challenge
await page.solveRecaptchas()
Now, wait for the solution and click on the submit button.
// Wait for the navigation and click the submit button
await Promise.all([
await Promise.all([
page.waitForNavigation(),
page.click(`#recaptcha-demo-submit`)
])
The complete code should be this:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer-extra')
const RecaptchaPlugin = require('puppeteer-extra-plugin-recaptcha')
// Use the RecaptchaPlugin with the specified provider (2captcha) and token
puppeteer.use(
RecaptchaPlugin({
provider: {
id: '2captcha',
token: 'XXXXXXX'
},
visualFeedback: true // Enable visual feedback (colorize reCAPTCHAs)
})
)
// Launch a headless browser instance
puppeteer.launch({ headless: true }).then(async browser => {
// Create a new page
const page = await browser.newPage()
// Navigate to a page containing a reCAPTCHA challenge
await page.goto('https://2captcha.com/demo/recaptcha-v2')
// Automatically solve the reCAPTCHA challenge
await page.solveRecaptchas()
// Wait for the navigation and click the submit button
await Promise.all([
page.waitForNavigation(),
page.click(`#recaptcha-demo-submit`)
])
// Take a screenshot of the response page
await page.screenshot({ path: 'response.png', fullPage: true })
// Close the browser
await browser.close()
})
Here's the outcome:
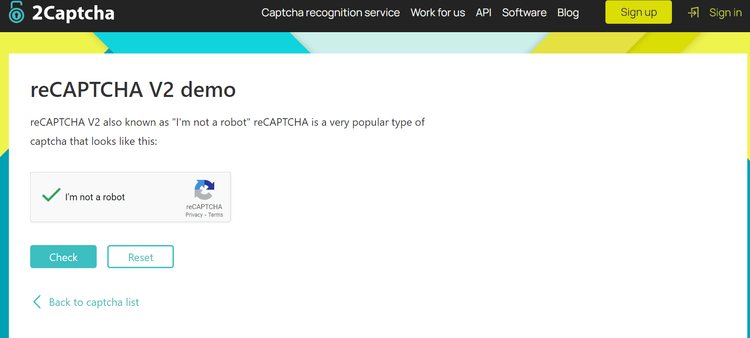
Great! You won over the obstacle.
However, using CAPTCHA solvers with Puppeteer works mostly for testing purposes rather than large-scale scraping, as it can quickly become too expensive and slow. For this reason, we'll focus on avoiding the appearance of the challenge (and re-trying our request when hit by it) by masking Puppeteer better.
Method #3: Supercharge Puppeteer with Stealth to Bypass CAPTCHA
There are two main approaches to bypassing CAPTCHAs with Puppeteer, as discussed: solving and avoiding. It's time to explore the second method and make your scraper undetectable.
Puppeteer Stealth is a plugin that includes several features that tackle the majority of methods websites use to detect headless Chrome. Let's see how it does that by scraping OpenSea, an anti-bot-protected site that presents CAPTCHAs when a request doesn't meet its natural user threshold.
To get started, you have to install puppeteer-extra and puppeteer-extra-plugin-stealth:
npm install puppeteer-extra puppeteer-extra-plugin-stealth
Then, import the modules, save the library into executablePath, and enable puppeteer-stealth using puppeteer.use(pluginStealth()):
const puppeteer = require("puppeteer-extra");
const pluginStealth = require("puppeteer-extra-plugin-stealth");
//save to executable path
const { executablePath } = require("puppeteer");
// Use stealth
puppeteer.use(pluginStealth());
The next steps include setting the viewport, navigating to the page URL, waiting for it to load, and taking screenshots to track the process.
// Launch puppеteer-stealth
puppeteer.launch({ executablePath: executablePath() }).then(async browser => {
// Create a new page
const page = await browser.newPage();
// Set page view
await page.setViewport({ width: 1280, height: 720 });
// navigate to the website
await page.goto("https://www.opensea.io/");
// Wait for page to load
await page.waitForTimeout(1000);
// Take a screenshot
await page.screenshot({ path: "image.png" });
// Close the browser
await browser.close();
});
Here's the complete code:
const puppeteer = require("puppeteer-extra");
// Add stealth plugin and use defaults
const pluginStealth = require("puppeteer-extra-plugin-stealth");
const { executablePath } = require("puppeteer");
// Use stealth
puppeteer.use(pluginStealth());
// Launch puppeteer-stealth
puppeteer.launch({ executablePath: executablePath() }).then(async browser => {
// Create a new page
const page = await browser.newPage();
// Set page view
await page.setViewport({ width: 1280, height: 720 });
// navigate to the website
await page.goto("https://www.opensea.io/");
// Wait for page to load
await page.waitForTimeout(1000);
// Take a screenshot
await page.screenshot({ path: "image.png" });
// Close the browser
await browser.close();
});
What about the result? See below.
Congrats! You're one step closer to becoming a web scraping expert. You've just made your spider more undetectable.
However, more advanced website protections can detect Puppeteer Stealth. Let's confirm that by running the same script on a G2's product page:
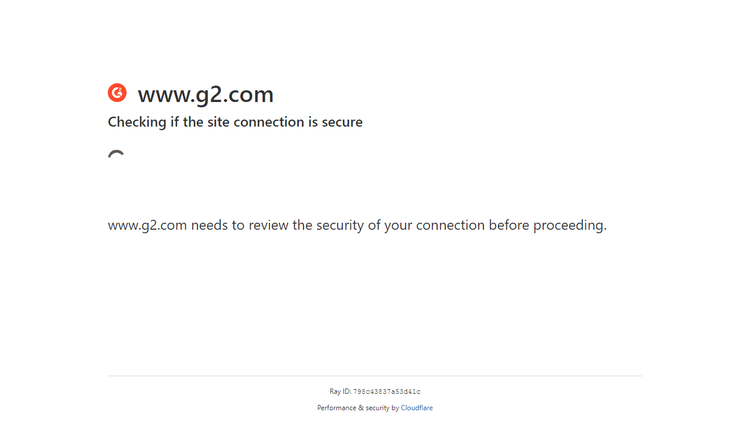
So far, base Puppeteer, puppeteer-extra-plugin-recaptcha and 2Captcha together don't solve the scraping scalability problem. We'll take a look at a final solution next.
Method #4: Best CAPTCHA Bypass with ZenRows
Puppeteer is a powerful tool but, as seen in the examples above, it comes with its own set of limitations. Shall we look for an alternative?
ZenRows is an all-in-one tool that enables large-scale scraping, including headless browser and anti-CAPTCHA features, in a single API call. Let's see it in action! We'll try to scrape the G2's page where Puppeteer Stealth failed.
To get started, sign up for your free API key.
You'll get to the Request Builder, where you have to paste https://www.g2.com/products/asana/reviews as a target URL and activate Antibot, JavaScript Rendering and Premium Proxy. In this case, we'll use the SDK mode.
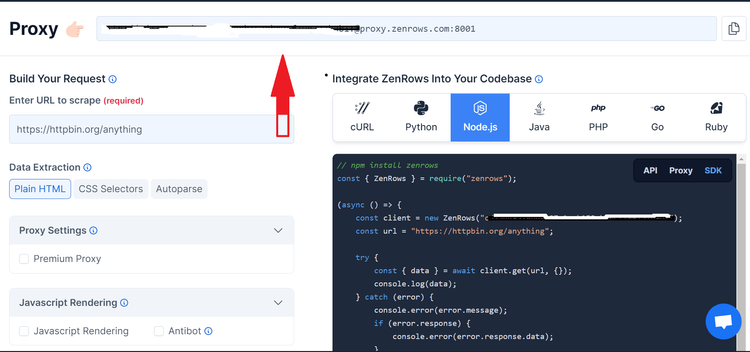
Now, switch to your code editor and install ZenRows using the npm command.
npm install zenrows
Lastly, paste the provided code on the Request Builder and console.log() the response.
const { ZenRows } = require("zenrows");
(async () => {
const client = new ZenRows("YOUR_API_KEY");
const url = "https://www.g2.com/products/asana/reviews";
try {
const { data } = await client.get(url, {
"js_render": "true",
"antibot": "true",
"premium_proxy": "true"
});
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.message);
if (error.response) {
console.error(error.response.data);
}
}
})();
Here's the successful outcome:
<!DOCTYPE html><html class=" cors history json svg es6object promises cssgradients fontface csstransitions"><head><style type="text/css">.turbo-progress-bar {
position: fixed;
display: block;
top: 0;
left: 0;
height: 3px;
background: #0076ff;
z-index: 9999;
transition:
width 300ms ease-out,
opacity 150ms 150ms ease-in;
transform: translate3d(0, 0, 0);
}
</style><meta charset="utf-8"><link href="https://www.g2.com/assets/favicon-fdacc4208a68e8ae57a80bf869d155829f2400fa7dd128b9c9e60f07795c4915.ico" rel="shortcut icon" type="image/x-icon"><title>Business Software and Services Reviews | G2</title><meta content="78D210F3223F3CF585EB2436D17C6943" name="msvalidate.01"><meta content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" name="viewport"><meta content="GNU Terry Pratchett" http-equiv="X-Clacks-Overhead"><meta content="ie=edge" http-equiv="x-ua-compatible"><meta content="en-us" http-equiv="content-language"><meta content="website" property="og:type"><meta content="G2" property="og:site_name"><meta content="@G2dotcom" name="twitter:site"><meta content="Business Software and Services Reviews | G2" property="og:title"><meta content="https://www.g2.com/" property="og:url"><meta content="Compare the best business software and services based on user ratings and social data. Reviews for CRM, ERP, HR, CAD, PDM and Marketing software." property="og:description">
Yay! You're all set. ZenRows made bypassing CAPTCHAs and advanced anti-bot detections very easy and quick.
Conclusion
Some solutions to bypass CAPTCHA with Puppeteer include integrating a solver and masking the browser better, yet they fail to deliver on a number of occasions and don't scale up.
For your successful data extraction project, you need a scalable and efficient solution like ZenRows, which handles all anti-bot bypasses for you in a single API call. Get your API key now and enjoy 1,000 requests for free.
Did you find the content helpful? Spread the word and share it on Twitter, or LinkedIn.