Struggling to find the best Python web scraping library to use? You aren't alone. Settling for a scraping library can get pretty troublesome if it fails because it's slow or easily detected by anti-bots.
A good Python library for web scraping should be fast, scalable and capable of crawling any type of web page. In this article, we'll discuss the seven best options, their pros and cons, as well as some quick examples to help you understand how they work.
What Are the Best Python Web Scraping Libraries
We did some background tests to check and verify which Python web scraping library is capable of scraping a web page without problems.
The best ones are the best ones:
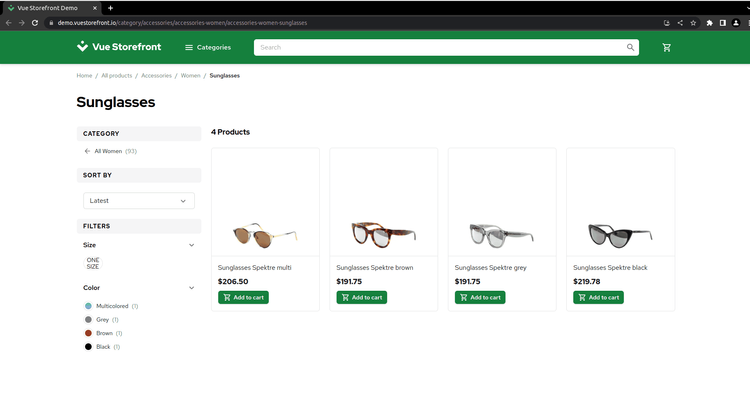
Let's go into detail and discuss these libraries with some Python web scraping examples. We'll extract the product details on the Vue Storefront with each.
1. ZenRows
ZenRows API is a Python web scraping library capable of solving the biggest scraping problem: getting blocked. Its features include rotating and premium proxies, a headless browser, geo-targeting, JavaScript rendering, and more. Using ZenRows saves you frustration, time and resources.
👍 Pros:
- ZenRows is easy to use.
- It can efficiently bypass CAPTCHAs and anti-bots.
- It offers smart rotating proxies.
- It can scrape JavaScript-rendered pages.
- It also works with other libraries.
👎 Cons:
- It's a paid service, but it comes with a free trial.
How to scrape a web page with ZenRows
Step 1: Generate the Python code
Create a free ZenRows account and you'll get to the Request Builder page. There, enter your target website's URL (VueStore), activate JavaScript rendering and select Python.
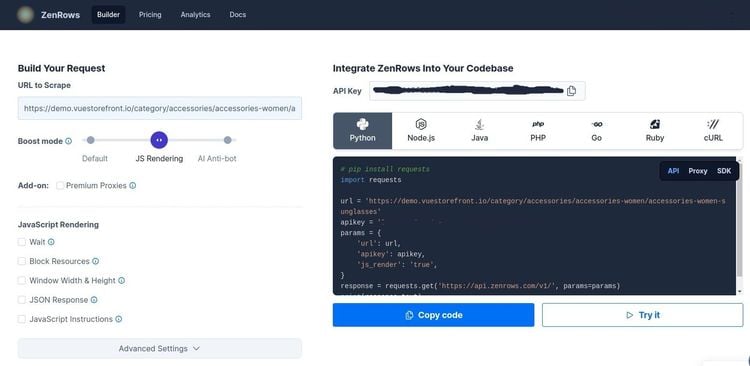
On the right, you should get a code like the one below. You can save it in a file named "scraper.py`.
# pip install requests
import requests
url = "https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses/"
apikey = "<YOUR_ZENROWS_API_KEY>"
params = {
"url": url,
"apikey": apikey,
"js_render": "true",
}
response = requests.get("https://api.zenrows.com/v1/", params=params)
Step 2: Parse the response
We'll use BeautifulSoup for parsing the generated HTML. The library has different methods, like find and find_all, that can help get elements with specific IDs or classes from the HTML tree.
Go ahead and import the library, then create a new BeautifulSoup object by passing the extracted data from the URL. Next, assign a second parameter, the parser, which can be html.parser, xml or lxml.
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
category = soup.find("section", {"class": "grid"})
for item in category.find_all("a", {"data-testid": "link"}):
print(item.text)
It'll return a list of all the anchor tags with the specified attributes found on the document and, using a simple for loop, the desired information is printed to the screen.
This is your final script:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = "https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses/"
apikey = "<YOUR_ZENROWS_API_KEY>"
params = {
"url": url,
"apikey": apikey,
"js_render": "true",
}
response = requests.get("https://api.zenrows.com/v1/", params=params)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
category = soup.find("section", {"class": "grid"})
for item in category.find_all("a", {"data-testid": "link"}):
print(item.text)
Run it, and congratulations! You have successfully scraped a web page using ZenRows. Here's what the output looks like:
Sunglasses Spektre multi
Sunglasses Spektre brown
Sunglasses Spektre grey
Sunglasses Spektre black
2. Selenium
Selenium is a widely used Python scraping library to scrape dynamic web content. It mimics human interactions by clicking a button, filling forms and more.
Selenium is compatible with many browsers, like Chrome and Firefox, allowing you to choose the one that suits your web scraping project the most. This flexibility helps ensure consistent results across different browser environments.
👍 Pros: It can scrape dynamic web pages. Multi-browser support.
👎 Cons: Selenium can be slow. It can't get status codes. It's time and resource-consuming.
To use selenium, update your scraper.py file and paste this code:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
url = "https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses/"
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get(url)
items = driver.find_elements(By.CSS_SELECTOR, ".grid a[data-testid='link']")
for item in items:
print(item.text)
After running the code, you should see the names of the four items printed on the console:
Sunglasses Spektre multi
Sunglasses Spektre brown
Sunglasses Spektre grey
Sunglasses Spektre black
And there you have it!
3. Requests
Requests is a user-friendly web scraping library in Python built on top of urllib3. It can directly get a URL without a PoolManager instance. Also, once you make a GET request, you can access the web page's contents by using the content property on the response object.
It simplifies the process of sending HTTP requests and handling responses, making it easier for developers to interact with web services and APIs.
👍 Pros:
- It doesn't require
PoolManager. - It's fast.
- It's easily understandable.
👎 Cons:
- It can't scrape interactive or dynamic sites with JavaScript.
- It's not good for sensitive information as it might be retained in the browser's memory.
How to scrape a web page using Requests
Let's work with a Vue Storefront page. The titles for each of the four items on the page are enclosed within anchor tags that have the attribute data-testid set to link within the element with the class grid.
Step 1: Get the main contents with the GET method
Use this code:
import requests
r = requests.get('https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses')
The GET method returns a response object. You can obtain the status code with the status_code property (in this case, it returns code 200) and the HTML data with the content property from it. The response object is saved in the variable r.
Step 2: Extract the specific information with BeautifulSoup
Extract the desired information by using the select method on the BeautifulSoup object, targeting anchor tags with the attribute data-testid set to link within elements having the class grid.
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.content, 'html.parser')
for item in soup.select('.grid a[data-testid="link"]'):
print(item.text)
That will return a list of all the anchor tags with specified attribute found on the document and, using a simple for loop, you can print the desired information on the screen. Update your scraper.py file with the following code::
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get('https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses')
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.content, 'html.parser')
for item in soup.select('.grid a[data-testid="link"]'):
print(item.text)
Congratulations! You made it; you've successfully used the Request Python library for web scraping. Your output should look like this:
Sunglasses Spektre multi
Sunglasses Spektre brown
Sunglasses Spektre grey
Sunglasses Spektre black
4. Beautiful Soup
Beautiful Soup is a powerful Python web scraping library, particularly for parsing XML and HTML documents. Its convenience is one of its most popular perks. Beautiful Soup is built on well-known Python parsing packages and allows you to try different techniques.
With Beautiful Soup, you can scan an already-parsed document and identify all the data under a particular type or format. It has great encoding detection capabilities.
👍 Pros:
- Easy to use and navigate.
- Extensible functionalities.
- Active community support.
- Detailed documentation.
👎 Cons:
- Limited support.
- You need to install multiple dependencies.
More: Take a look at our Beautiful Soup web scraping tutorial to learn to use this Python library.
5. Playwright
Playwright is an open-source web scraping library that makes it easier to extract data from websites across different browsers, as it provides an excellent cross-browser automation solution.
Although Playwright is user-friendly, its concepts and features might still require some time to properly understand. And because it needs to run different browser instances, it consumes more memory than other libraries.
👍 Pros:
- Cross-browser support.
- High-level API.
- Powerful selector engine.
- Headless mode.
👎 Cons:
- It's resource-intensive.
- Continuous maintenance or updates.
- Steep learning curve.
More: Check out of Playwright web scraping tutorial to get started.
6. Scrapy
Scrapy is a high-level framework used to scrape data from highly complex websites. With it, bypassing CAPTCHAs using predefined functions or external libraries is possible.
You can write a simple Scrapy crawler to scrape web data by using an object definition by means of a Python class. However, it's not particularly user-friendly compared to other Python scraping libraries.
Although the learning curve for this library is steep, you can do a lot with it, and it's highly efficient in performing crawling tasks.
👍 Pros:
- General framework for scraping purposes.
- Strong encoding support.
- It doesn't require BeautifulSoup.
👎 Cons:
- Steep learning curve.
- Scrapy can't scrape dynamic web pages.
- It requires different installation steps for different websites.
How to scrape a web page using Scrapy
Step 1: Create a Spider class
Make a new class named AccessorySpider and give it the parameter scrapy.Spider. Inside the class, define the name as mySpider, and start_urls as a list of the URLs to scrape.
import scrapy
class AccessorySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name='mySpider'
start_urls = ['https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses',]
Step 2: Define the parse method
The parse method takes a response parameter, and you can retrieve each item with the CSS method on the response object. The CSS method can take the css selector of the item class as its parameter:
response.css('.grid a[data-testid="link"]')
To retrieve all the items with that class, make a for loop and print the contents with the XPath method:
for item in response.css('.grid a[data-testid="link"]'):
print(item.xpath('string(.)').get())
Update your scraper.py file using the following code:
import scrapy
class AccessorySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name='mySpider'
start_urls = ['https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses']
def parse(self, response):
for item in response.css('.grid a[data-testid="link"]'):
print(item.xpath('string(.)').get())
Run the spider by executing the following script in the terminal, and you should see the list of items printed on the screen:
Sunglasses Spektre multi
Sunglasses Spektre brown
Sunglasses Spektre grey
Sunglasses Spektre black
That's it!
7. urllib3
urllib3 is an HTTP client known for its reliability, performance optimizations, and extensive features. It provides a solid foundation for making HTTP requests and is often used by other Python web scraping libraries or frameworks.
It works with a PoolManager instance (class), a response object that manages connection pooling, and thread safety.
👍 Pros:
- Extensibility.
- Good community support.
- It handles concurrency with
PoolManager.
👎 Cons:
- Complicated syntax compared to other libraries like Requests.
- urllib3 can't extract dynamic data.
How to scrape a web page using urllib3
Step 1: Create a PoolManager instance
Import the urllib3 library, then create a PoolManager instance and save it to a variable called http:
import urllib3
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
Once a PoolManager instance is created, you can make an HTTP GET request by using the request() method on it.
Step 2: Make a GET request
Use the request method on the PoolManager instance. You can give the request method two parameters to make a simple GET request. For that case, the first is the string GET, and the second is the string given by the URL you want to scrape:
r = http.request('GET', 'https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses')
Step 3: Extract the data from the response object
The request response is given by an HTTPResponse object, and from it, you can obtain information such as the status code. Let's get the data by using the data method on the response object and BeautifulSoup:
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.data, 'html.parser')
To extract the data, use a for loop with the select method and the item’s css selector:
for item in soup.select('.grid a[data-testid="link"]'):
print(item.text)
Update your scraper.py file with the following code:
import urllib3
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
r = http.request('GET', 'https://demo.vuestorefront.io/category/accessories/accessories-women/accessories-women-sunglasses')
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.data, 'html.parser')
for item in soup.select('.grid a[data-testid="link"]'):
print(item.text)
And that's it! You have successfully scraped the data from the accessories category on the Vue Storefront using the urllib3 Python web scraping library:
Sunglasses Spektre multi
Sunglasses Spektre brown
Sunglasses Spektre grey
Sunglasses Spektre black
Conclusion
Different Python web scraping libraries can simplify the scraping process. We've shared the seven best ones, and here are some features worth mentioning:
| Library | Ease of use | Performance | Dynamic Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZenRows | Easy to use | It's fast for static content and moderate for dynamic content. Consumes fewer resources compared to other libraries | ✅ |
| Selenium | Quite difficult to use compared to libraries like Requests and urllib3 | Slow and consumes high resources | ✅ |
| Requests | One of the easiest web scraping libraries to use but have fewer capabilities | Fast and low resource consumption | - |
| Beautiful Soup | Convenient and easy to use | It consumes memory quickly | - |
| Playwright | Easy to use | Resource intensive | ✅ |
| Scrapy | Difficult to learn compared to the other Python web scraping libraries | Fast and medium resource consumption | - |
| urllib3 | Similar to requests but with a lower-level API | It's fast and consumes low resources | - |
A common problem with web scraping libraries for Python is their inability to avoid bot detection while scraping a web page, making scraping difficult and stressful.
ZenRows solves this problem with a single API call. Take advantage of the 1,000 API credits you get for free upon registration.
Frequent Questions
Why Are Python Libraries for Web Scraping Important?
Python is one of the most popular languages developers use to build web scrapers. That's because its classes and objects are significantly easier to use than any other language.
However, building a custom Python web crawler from scratch can will be difficult, especially if you want to scrape many custom websites and bypass anti-bot measures. Python web crawling libraries simplify and cut down the lengthy process.
Which Libraries Are Used for Web Scraping In Python?
There are many Python web scraping libraries to choose from. The most reliable options are:
- ZenRows.
- Selenium.
- Requests.
- Beautiful Soup.
- Playwright.
- Scrapy.
- urllib3.
What Is the Best Python Web Scraping Library?
The best Python web scraping library to use is ZenRows. Other libraries can get the job done too, but the time and effort spent on learning these tools and the possibility of getting your scraper blocked can be avoided easily with it.
What Is the Most Popular Python Library For Web Scraping?
The Requests library is one of the most used web scraping libraries since it helps make basic requests for further analysis.
What Is the Fastest Python Web Scraping Library?
ZenRows is the fastest Python web scraping library if you consider the time and effort it saves dealing with anti-bot measures.
Did you find the content helpful? Spread the word and share it on Twitter, or LinkedIn.