A third of the top 100,000 websites use CAPTCHAs to stop bot traffic, so they've probably complicated your scraping plans at some time.
The challenges are designed as a gate to let humans in and keep bots out, but does that mean you can't win over them? Luckily, you can! Today, you'll learn how to bypass CAPTCHA with Selenium in Python using three different methods:
Cool? Let's dive in. 🚀
Can Selenium Bypass CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHAs usually appear when the visitor exhibits suspiciously bot-like behavior, such as visiting many pages without scrolling, but Selenium can help here.
There are two main approaches to get rid of the tests: you can solve them by paying humans (expensive at scale, yet sometimes useful), or prevent them from appearing by implementing advanced techniques (and retrying your request if any fail). Selenium allows you to interact with the form in the first case and make your traffic look more human in the second.
Method #1: Bypass CAPTCHA with Selenium and 2Captcha
Let's imagine you need to resolve a CAPTCHA, for example, to submit a form. We'll do that with a popular service called 2captcha to handle CAPTCHA in Selenium using a demo page.
We'll explore how the service works against a popular CAPTCHA challenge. So, let's get started by installing some dependencies. If you don't have them yet, run the command pip install selenium 2captcha-python and import some modules as shown below.
Note: In the past, installing WebDriver was a mandatory step, but this is no longer the case. Selenium version 4 and higher come with WebDriver built-in by default. If you have an older Selenium version, upgrading is recommended to access the latest features and capabilities. You can check your current version with the command pip show selenium and update to the latest version using pip install --upgrade selenium.
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from twocaptcha import TwoCaptcha
from selenium import webdriver
import time
Then, open a Chrome instance and navigate to the demo page.
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
url = "https://2captcha.com/demo/normal"
driver.get(url)
The next step is to locate the CAPTCHA image and pass its URL to the solver.normal() method, which returns the text solution. Save it in the result variable.
imgResults = driver.find_elements(By.XPATH,"//img[contains(@class,'_2hXzbgz7SSP0DXCyvKWcha')]")
solver = TwoCaptcha(Your_2Captcha_API_key)
result=solver.normal(imgResults[0].get_attribute('src'))
print ('solved: ' + str(result))
The following task is to find the input field, fill it with the solution text received by the 2Captcha service, and click the submit button.
To end, locate the <p> element on the page and print its message. You should get ''Captcha is passed successfully!'' in case of success.
messagefield=driver.find_element(By.XPATH,"//p[contains(@class,'_2WOJoV7Dg493S8DW_GobSK')]")
print (messagefield.text)
Here's the complete code:
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from twocaptcha import TwoCaptcha
from selenium import webdriver
import time
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
url = "https://2captcha.com/demo/normal"
driver.get(url)
imgResults = driver.find_elements(By.XPATH,"//img[contains(@class,'_2hXzbgz7SSP0DXCyvKWcha')]")
solver = TwoCaptcha(Your_2Captcha_API_key)
result = solver.normal(imgResults[0].get_attribute("src"))
print ("solved: " + str(result))
captchafield = driver.find_element(By.XPATH,"//input[contains(@class,'_26Pq0m_qFk19UXx1w0U5Kv')]")
captchafield.send_keys(result["code"])
button = driver.find_element(By.XPATH,"//button[contains(@class, 'l2z7-tVRGe-3sq5kU4uu5 _2xjDiWmBxfqem8nGQMmGci _2HIb5VBFp6Oi5_JoLdEcl6 _2vbG_IBm-DpI5KeEAHJkRy')]")
button.click()
time.sleep(10)
messagefield=driver.find_element(By.XPATH,"//p[contains(@class,'_2WOJoV7Dg493S8DW_GobSK')]")
print (messagefield.text)
And here's the output:
solved: {'captchaId': '72848141048', 'code': 'W9H5K'}
Captcha is passed successfully!
Congratulations! You solved your first CAPTCHA with Selenium and 2Captcha.
However, using paid solvers is hard to scale up since it's expensive and slow, and they only work with a fraction of all CAPTCHA types. Therefore, let's see an alternative next.
Method #2: Implement Selenium Stealth
The use of Selenium is easy to be identified since its base version sends some clear bot signals, such as its User-Agent name, which might easily prompt a CAPTCHA. And to prove this, let's try to access OpenSea, a protected site.
For that, create a headless Chrome instance, pass the target URL to the get() function to wait for the page to load, and take a screenshot.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
import time
options = Options()
options.add_argument("--headless")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)
driver.get("https://opensea.io/")
time.sleep(30)
driver.save_screenshot("opensea.png")
driver.close()
What's the result?
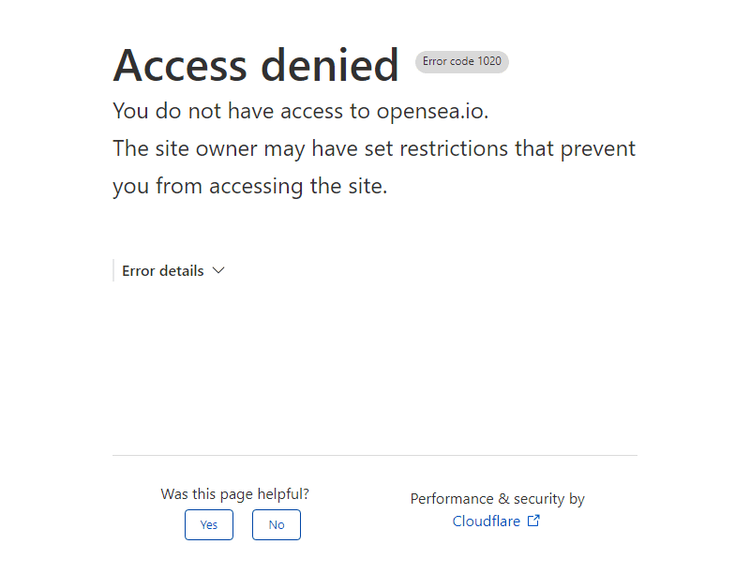
Access denied! OpenSea detected non-human traffic and blocked our bot. This is where the selenium-stealth, a Python package that helps avoid detection when scraping with Selenium, comes to the rescue. It will make your traffic look more manual and prevent getting blocked, i.e. with CAPTCHAs.
To start with, install the Stealth package: pip install selenium-stealth
Then, import some necessary libraries and configure the driver to run Chrome in headless mode. Next, configure, exclude the enable-automation, and disable the useAutomationExtension since websites detect bot traffic with those flags.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
import time
from selenium_stealth import stealth
options = Options()
options.add_argument("--headless")
options.add_experimental_option("excludeSwitches", ["enable-automation"])
options.add_experimental_option("useAutomationExtension", False)
The following step creates a ChromeDriver instance with custom options:
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)
Now, let's use the stealth() function to set custom Chrome webdriver configurations to make our bot less detectable. For example, we'll set a user agent string, which is sent along with the HTTP request.
stealth(driver,
user_agent = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/110.0.5481.105 Safari/537.36',
languages=["en-US", "en"],
vendor="Google Inc.",
platform="Win32",
webgl_vendor="Intel Inc.",
renderer="Intel Iris OpenGL Engine",
fix_hairline=True,
)
The script then navigates to the target page, waits for it to load, and screenshots it.
driver.get("https://opensea.io/")
time.sleep(30)
driver.save_screenshot("opensea.png")
driver.close()
Here's the full code:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
import time
from selenium_stealth import stealth
options = Options()
options.add_argument("--headless")
options.add_experimental_option("excludeSwitches", ["enable-automation"])
options.add_experimental_option("useAutomationExtension", False)
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)
stealth(driver,
user_agent = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/110.0.5481.105 Safari/537.36',
languages=["en-US", "en"],
vendor="Google Inc.",
platform="Win32",
webgl_vendor="Intel Inc.",
renderer="Intel Iris OpenGL Engine",
fix_hairline=True,
)
driver.get("https://opensea.io/")
time.sleep(30)
driver.save_screenshot("opensea2.png")
driver.close()
Let's look at the output:
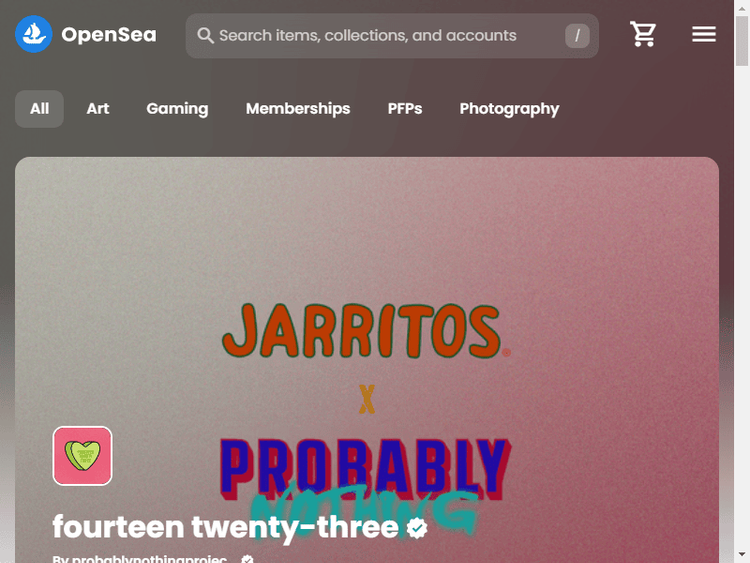
Success! This helps bypass CAPTCHA with Selenium. You might also want to look at our guide on bypassing blocks with Selenium's Undetected ChromeDriver.
However, would Selenium Stealth work scraping sites with the toughest anti-bot protections? Try with a product review page on G2, and you'll get the answer.
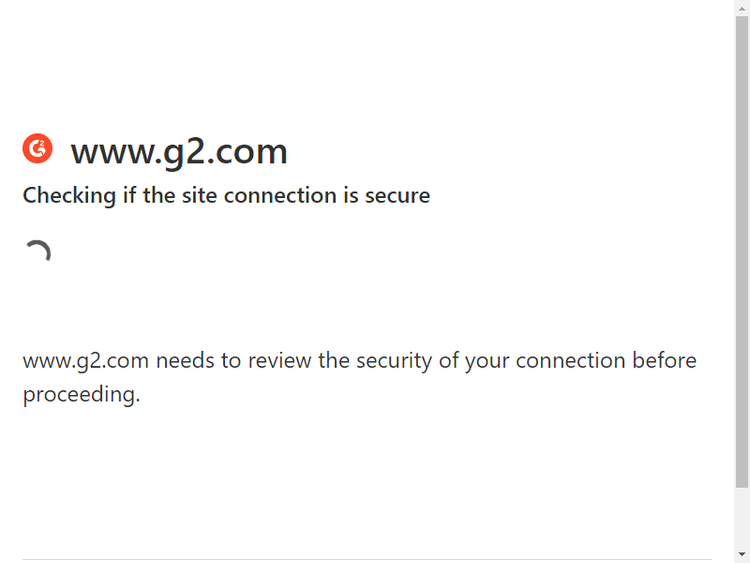
As the two methods turned out to be enough to bypass CAPTCHA with Selenium, we should explore a better option.
Method #3: Bypass CAPTCHA with ZenRows API
Scraping content from websites with advanced protection requires the right tool. ZenRows is a powerful anti-bot API that gives you headless browser functionality and also enables large-scale scraping by getting rid of anti-bot protections, including CAPTCHA.
Let's see how easy it's to scrape content from G2 using ZenRows.
First, sign up for your free API key. You'll get to the Request Builder, where you have to input <https://www.g2.com/products/asana/reviews> as a target URL and then activate Premium Proxy, JavaScript Rendering, and Antibot.
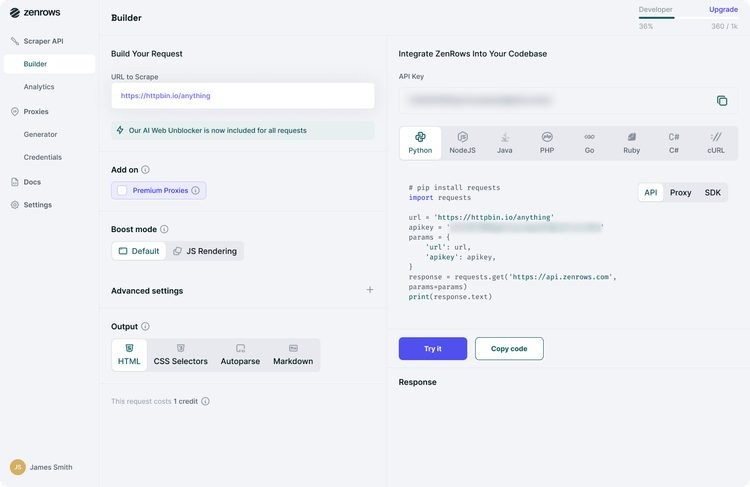
Second, copy and paste the API request code to your Python IDE. It should look like this:
# python3 and requests library required
# pip install requests
import requests
response = requests.get("https://api.zenrows.com/v1/?apikey=Your_ZenRows_API_Key&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.g2.com%2Fproducts%2Fasana%2Freviews%2F&js_render=true&antibot=true&premium_proxy=true")
print(response.text)
Third and lastly, execute the code and watch as it prints G2's HTML.
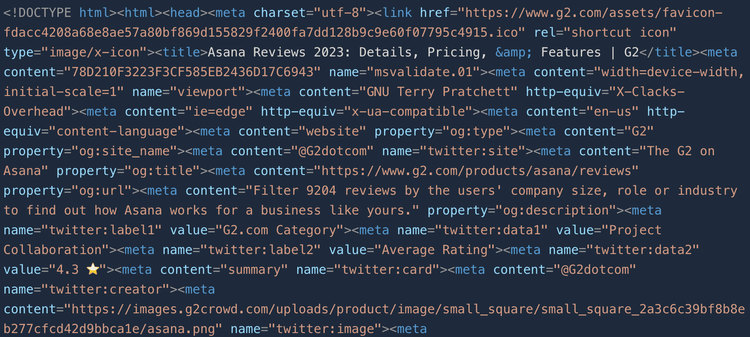
That's how easy it is. 😀 Yay!
Conclusion
We've seen how to bypass CAPTCHA with Selenium using a paid solver, but using it as a stand-alone solution proved to be unreliable and expensive. Then, we installed a plugin to base Selenium that might help with large-scale scraping, yet it fell short.
For successful data retrieval, you need a powerful tool to rely completely on in order to handle CAPTCHA. ZenRows provides an easy-to-setup API that enables you to overcome all anti-bot challenges, and you can try it for free today.
Did you find the content helpful? Spread the word and share it on Twitter, or LinkedIn.